x
هدف البحث
بحث في العناوين
بحث في المحتوى
بحث في اسماء الكتب
بحث في اسماء المؤلفين

اختر القسم
موافق


Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar


literature


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced
Reported Speech
المؤلف:
MYENGLISHPAGES.COM
المصدر:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
17-6-2021
1977
Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)
What is reported speech?
Reported speech is when you tell somebody else what you or a person said before.
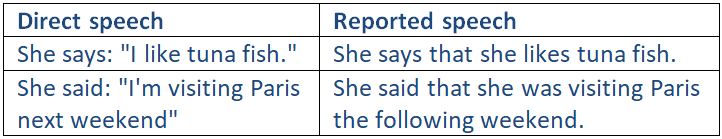
Distinction must be made between direct speech and reported speech.
Direct speech vs Reported speech:
Different types of sentences
When you use reported speech, you either report:
Statements
questions
requests / commands
other types
A. Reporting Statements
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
Pronouns
tense
place and time expression
1- Pronouns
In reported speech, you often have to change the pronoun depending on who says what.
Example:
She says, “My dad likes roast chicken.” – She says that her dad likes roast chicken.
2- Tenses
If the sentence starts in the present, there is no backshift of tenses in reported speech.
If the sentence starts in the past, there is often backshift of tenses in reported speech.
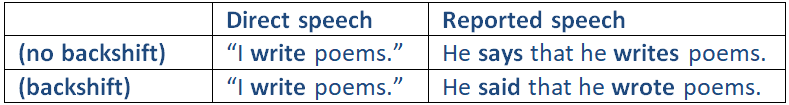
Do not change the tense if the introductory clause is in a present tense (e. g. He says). Note, however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person singular).No backshift
Example:
He says, “I write poems.” – He says that he writes English.
Backshift
You must change the tense if the introductory clause is in a past tense (e. g. He said).
Example:
He said, “I am happy.” – He said that he was happy.
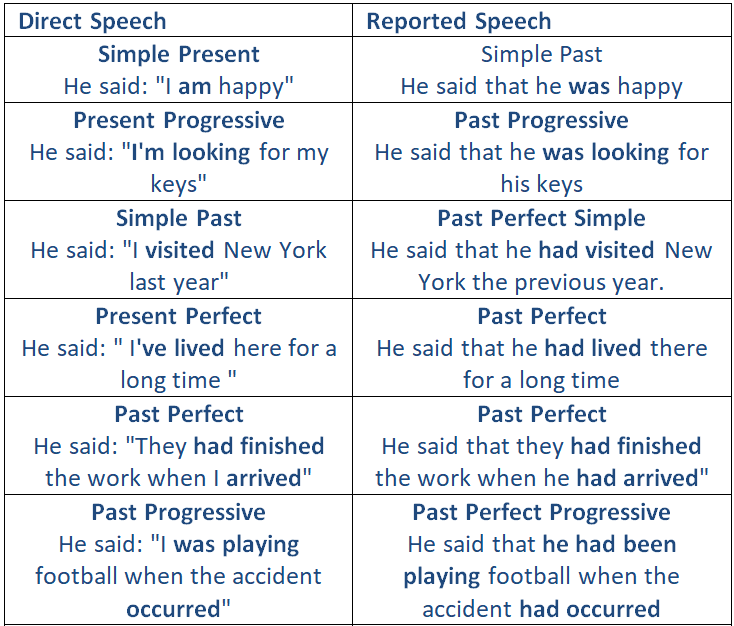
Examples of the main changes in tense:

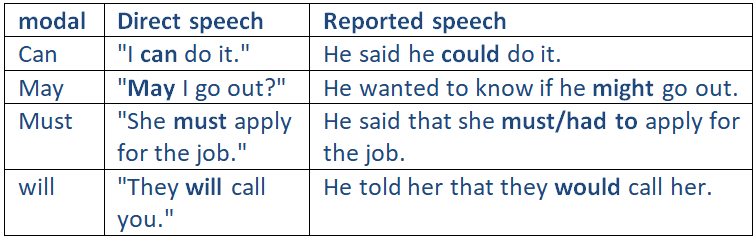
The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn't, ought to, used to do not normally change.
Example:
He said, "She might be right." – He said that she might be right.
Other modal verbs may change:
3- Place, demonstratives and time expressions
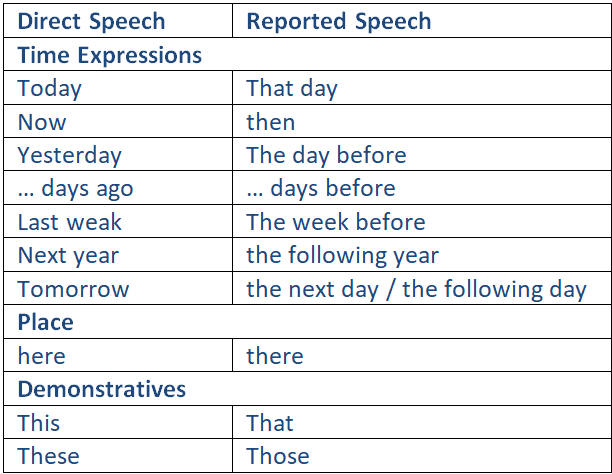
Place, demonstratives and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement (i.e. the location and/or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes of place; demonstratives and time expressions.
B. Reporting Questions
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
Pronouns
place and time expressions
tenses (backshift)
Also note that you have to:
. transform the question into an indirect question
. use the question word (where, when, what, how) or if / whether

C. Reporting requests / commands
When transforming requests and commands, check whether you have to change:
Pronouns
place and time expressions

Tenses are not relevant for requests – simply use to / not to + verb (infinitive without "to")
Example:
She said, “Sit down." - She asked me to sit down.
She said, "don't be lazy" - She asked me not to be lazy
For affirmative use to + infinitive (without to)
For negative requests, use not to + infinitive (without to).
D. Other transformations
Expressions of advice with must, should and ought are usually reported using advise / urge.
Example:
"You must read this book."
He advised / urged me to read that book.
The expression let’s is usually reported using suggest. In this case, there are two possibilities for reported speech: gerund or statement with should.
Example:
"Let’s go to the cinema."
1. He suggested going to the cinema.
2. He suggested that we should go to the cinema.
Main clauses connected with and/but
If two complete main clauses are connected with ‚and or ‚but, put ‚that after the conjunction.
Example:
He said ,“I saw her but she didn't see me.“ – He said that he had seen her but that she hadn't seen him.“
If the subject is dropped in the second main clause (the conjunction is followed by a verb), do not use ‚that‘.
Example:
She said,“I am a nurse and work in a hospital.“ – He said that she was a nurse and worked in a hospital.“