

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The chelate and macrocyclic effects
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص218-219
2025-09-01
93
The chelate and macrocyclic effects
Key points: The chelate and macrocyclic effects are the greater stability of complexes containing coordinated polydentate ligands compared with a complex containing the equivalent number of analogous monodentate ligands; the chelate effect is largely an entropic effect; the macrocyclic effect has an additional enthalpic contribution. When Kf1 for the formation of a complex with a bidentate chelate ligand, such as ethyl enediamine (en), is compared with the value of 2 for the corresponding bis(ammine) com plex, it is found that the former is generally larger:
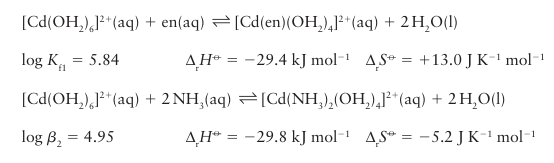
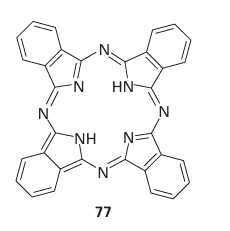
Two similar Cd N bonds are formed in each case, yet the formation of the chelate containing complex is distinctly more favourable. This greater stability of chelated complexes compared with their nonchelated analogues is called the chelate effect. The chelate effect can be traced primarily to differences in reaction entropy between chelated and nonchelated complexes in dilute solutions. The chelation reaction results in an increase in the number of independent molecules in solution. By contrast, the nonchelating reaction produces no net change (compare the two chemical equations above). The former therefore has the more positive reaction entropy and hence is the more favourable process. The reaction entropies measured in dilute solution support this interpretation. The entropy advantage of chelation extends beyond bidentate ligands, and ap plies, in principle, to any polydentate ligand. In fact, the greater the number of donor sites the multidentate ligand has, the greater is the entropic advantage of displacing monodentate ligands. Macrocyclic ligands, where multiple donor atoms are held in a cyclic array, such as crown ethers or phthalocyanin (77), give complexes of even greater stability than might otherwise be expected. This so-called macrocyclic effect is thought to be a combination of the entropic effect seen in the chelate effect, together with an additional energetic contribution that comes from the preorganized nature of the ligating groups (that is, no additional strains are introduced to the ligand on coordination). The chelate and macrocyclic effects are of great practical importance. The majority of reagents used in complexometric titrations in analytical chemistry are polydentate chelates like edta4 , and most biochemical metal binding sites are chelating or macrocylic ligands. A formation constant as high as 1012 to 1025 is generally a sign that the chelate or macro cyclic effect is in operation. In addition to the thermodynamic rationalization for the chelate effect we have described, there is an additional role in the chelate effect for kinetics. Once one ligating group of a polydentate ligand has bound to a metal ion, it becomes more likely that its other ligating groups will bind, as they are now constrained to be in close proximity to the metal ion; thus chelate complexes are favoured kinetically too.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















