

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
BUTADIENE
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 37
6-4-2016
1567
BUTADIENE (CH2=CH-CH=CH2)
Butadiene is by far the most important monomer for synthetic rubber production. It can be polymerized to polybutadiene or copolymerized with styrene to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). Butadiene is an important intermediate for the synthesis of many chemicals such as hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. Both are monomers for producing nylon. Chloroprene is another butadiene derivative for the synthesis of neoprene rubber.
The unique role of butadiene among other conjugated diolefins lies in its high reactivity as well as its low cost. Butadiene is obtained mainly as a coproduct with other light olefins from steam cracking units for ethylene production. Other sources of butadiene are the catalytic dehydrogenation of butanes and butenes, and dehydration of 1,4-butanediol. Butadiene is a colorless gas with a mild aromatic odor. Its specific gravity is 0.6211 at 20°C and its boiling temperature is –4.4°C. The U.S. production of butadiene reached 4.1 billion pounds in 1997 and it was the 36th highest-volume chemical.
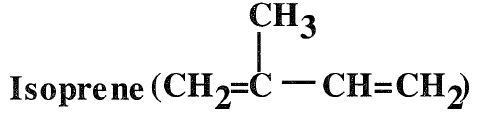
Isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene) is a colorless liquid, soluble in alcohol but not in water. Its boiling temperature is 34.1°C. Isoprene is the second important conjugated diene for synthetic rubber production. The main source for isoprene is the dehydrogenation of C5 olefins (tertiary amylenes) obtained by the extraction of a C5 fraction from catalytic cracking units. It can also be produced through several synthetic routes using reactive chemicals such as isobutene, formaldehyde, and propene . The main use of isoprene is the production of polyisoprene. It is also a comonomer with isobutene for butyl rubber production.















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















