

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Spinal Cord—Spinal Medulla
المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
6-8-2016
1872
Spinal Cord—Spinal Medulla
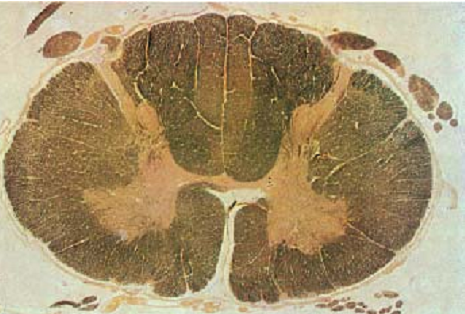
Cross-section of the cervical part (C5)—cervical intumescence .
The spinal medulla is traversed lengthwise by the columnar gray matter ( substantia grisea). It is completely envelope d by the white matter ( substantia alba, medullary sheath). The columnar gray matter displays a butterfly or H-pattern in cross-sections. There is a deep anterior median fissure (fissure mediana anterior ), the dorsal median fissure is not as deep ( sulcus medianu posterior ). The gray matter forms extensions, which look like horns in cross-sections. They are therefore named cornua. Both halves of the spinal medulla feature a larger anterior horn ( cornuanterius, columna anterior) and a slender posterior horn ( cornu posterior, columna posterior ). Both sides are connected via the central intermediary matter, which is joined in the center ( commissura grisea) with the central canal . The figure reveals that the posterior horns extend to the surface in the proximity of the posterior root of the spinal nerves. The tissue next to the spinal cord (stained brown) represents the rootlets of the posterior root of the spinal nerves ( fila radicularia ). The darker stained medullary sheath shows a clear substructure. This sheath contains the longitudinal, mostly myelinated nerve fibers of the various afferent and efferent projection tracts. The surface of the spinal cord is covered by the spinal piamater (stained soft yellow).
Stain: medullar y sheath preparation—Weiger t carmine; magnification: × 8
Spinal Cord—Spinal Medulla
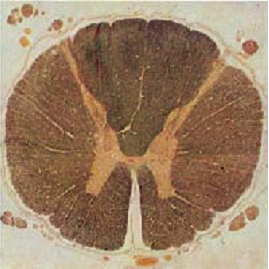
Cross-section of the thoracic part (T6). Note the delicate anterior and posterior horns of the gray matter. The gray matter protrudes slightly to the sides ( cornu laterale).
Stain: medullary sheath preparation—Weigert carmine; magnification: × 8
Spinal Cord—Spinal Medulla
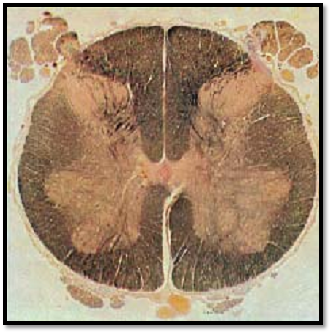
Cross-section of the lumbar part (L6)—lumbosacral intumescence.
The gray matter (anterior and posterior horns) is prominently expressed because the nerves for the extremities exit here.
Stain: medullar y sheath preparation—Weiger t carmine; magnification: × 8
Spinal Cord—Spinal Medulla
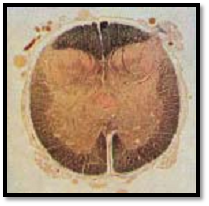
Cross-section of the sacral part (S3).
Massive posterior horns are characteristic of the sacral spinal medulla. There is a broad interface to the anterior horns. Note the very narrow medullary sheath.
Stain: medullar y sheath preparation—Weigert carmine; magnification: × 8
Spinal Cord—Spinal Medulla
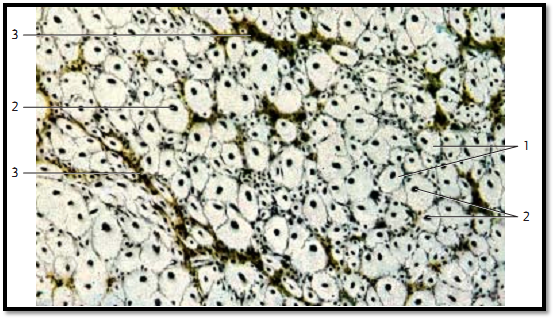
Cross-section of the white matter ( substantia alba ) of the spinal medulla. The medullary sheath consists pre dominantly of longitudinal myelinated nerve fibers. Their myelin sheaths 1 are colorless in this preparation and show a wide range of diameters. The dark spots inside the colorless (white) areas are silver impregnated axons 2 . Unmyelinated or sparsely myelinated axons occur sporadically. Delicate vascularized connective tissue septa 3 start at the surface and traverse the spinal white matter. This causes a subdivision of the medullary sheath into parcels.
1 Myelin sheaths
2 Axons (neurites)
3 Vascularized connective tissue septa
Stain: Bielschowsky -Gros silver impregnation; magnification: × 500
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















