

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Hydrotreatment Catalysts and Reactions
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 84
26-7-2017
1326
Hydrotreatment Catalysts and Reactions
Catalysts used in hydrotreatment (hydrodesulfurization, HDS) processes are the same as those developed in Germany for coal hydrogenation during World War II. The catalysts should be sulfur-resistant.
The cobalt-molybdenum system supported on alumina was found to be an effective catalyst. The catalyst should be reduced and sulfided during the initial stages of operation before use. Other catalyst systems used in HDS are NiO/MoO3 and NiO/WO3. Because mass transfer has a significant influence on the reaction rates, catalyst performance is significantly affected by the particle size and pore diameter.
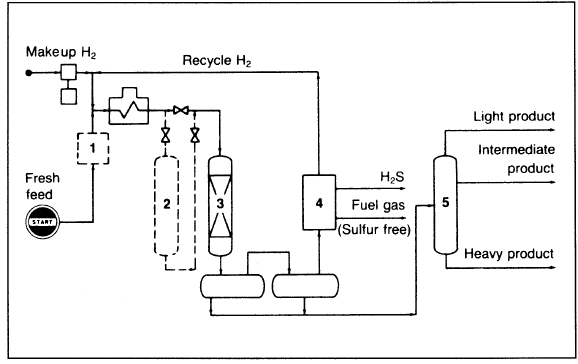
Figure 3-9. Flow diagram of an Exxon hydrotreating unit: (1) filter, (2) guard vessel to protect reactor, (3) main reactor, (4) gas treatment, (5) fractionator.
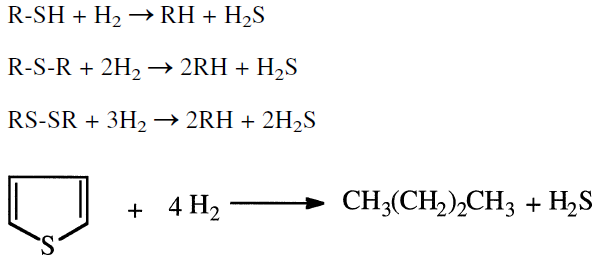
Reactions occurring in hydrotreatment units are mainly hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrogenation of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. In the first case H2S is produced along with the hydrocarbon. In the latter case, ammonia is released. The following examples are hydrodesulfurization reactions of some representative sulfur compounds present in petroleum fractions and coal liquids.
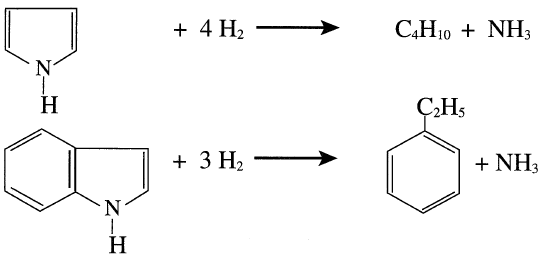
Examples of hydrodenitrogenation of two types of nitrogen compounds normally present in some light and middle crude distillates are shown as follows:
More complex sulfur and nitrogen compounds are present in heavy residues. These are hyrodesulfurized and hydrodenitrogenated, but under more severe conditions than normally used for lighter distillates. For example, for light petroleum distillates the approximate temperature and pressure ranges of 300–400°C and 35–70 atm. are used, versus 340–425°C and 55–170 atm. for heavy petroleum residua. Liquid hourly space velocities (LHSV) in the range of 2–10 hr–1 are used for light products, while it is 0.2–10 hr–1 for heavy residues.















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















