

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
LINEAR ALCOHOLS
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 207
28-8-2017
2125
LINEAR ALCOHOLS
Linear alcohols (Cl2-C26) are important chemicals for producing various compounds such as plasticizers, detergents, and solvents. They are also produced by the oligomerization of ethylene using aluminum alkyls (Ziegler catalysts). The Alfol process (Figure 1.1) for producing linear primary alcohols is a four-step process. In the first step, triethylaluminum is produced by the reaction of ethylene with hydrogen and aluminum metal:
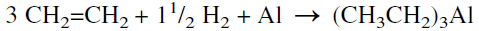
In the next step, ethylene is polymerized by the action of triethylaluminum at approximately 120°C and 130 atmospheres to trialkylaluminum. Typical reaction time is approximately 140 minutes for an average C12 alcohol production:
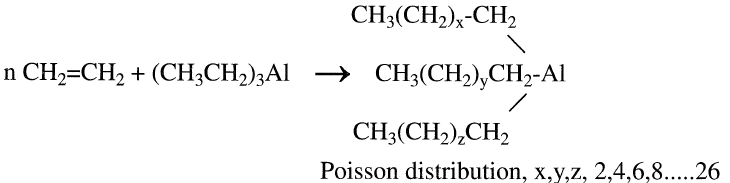
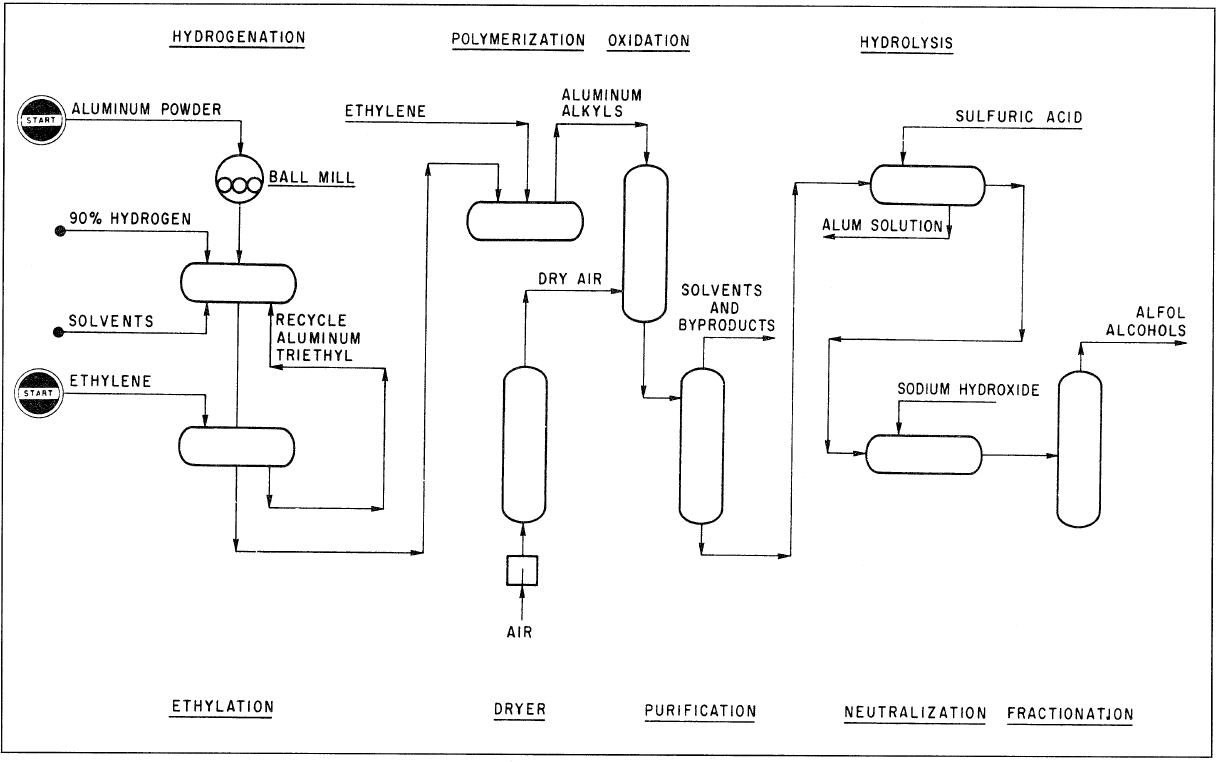
Figure 1.1. The Alfol process for making even-numbered straight-chain alpha alcohols.
The oxidation of triethylaluminum is carried out between 20–50°C with “bone dry” air to aluminum trialkoxides.
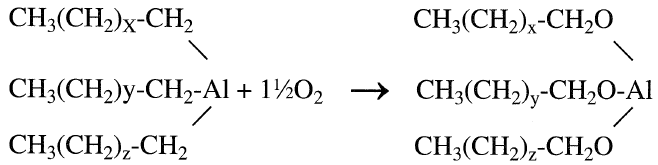
The final step is the hydrolysis of the trialkoxides with water to the corresponding even-numbered primary alcohols. Alumina is coproduced and is characterized by its high activity and purity:
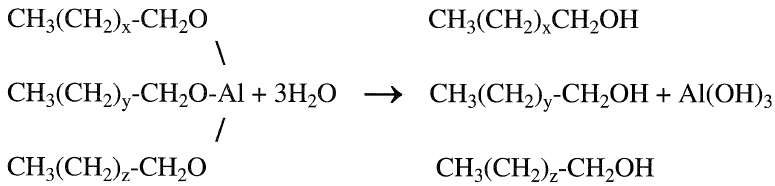
Linear alcohols in the range of Cl0–Cl2 are used to make plasticizers. Those in the range of Cl2–Cl6 are used for making biodegradable detergents.
They are either sulfated to linear alkylsulfates (ionic detergents) or reacted with ethylene oxide to the ethoxylated linear alcohols (nonionic detergents). The Cl6–Cl8 alcohols are modifiers for wash and wear polymers. The higher alcohols, C20–C26, are synthetic lubricants and mold release agents.















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















