


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 16-12-2019
Date: 16-12-2019
Date: 25-7-2018
|
Hydrolysis of proteins by boiling aqueous acid or base yields an assortment of small molecules identified as α-aminocarboxylic acids. More than twenty such components have been isolated, and the most common of these are listed in the following table. Those amino acids having green colored names are essential diet components, since they are not synthesized by human metabolic processes. The best food source of these nutrients is protein, but it is important to recognize that not all proteins have equal nutritional value. For example, peanuts have a higher weight content of protein than fish or eggs, but the proportion of essential amino acids in peanut protein is only a third of that from the two other sources. For reasons that will become evident when discussing the structures of proteins and peptides, each amino acid is assigned a one or three letter abbreviation.
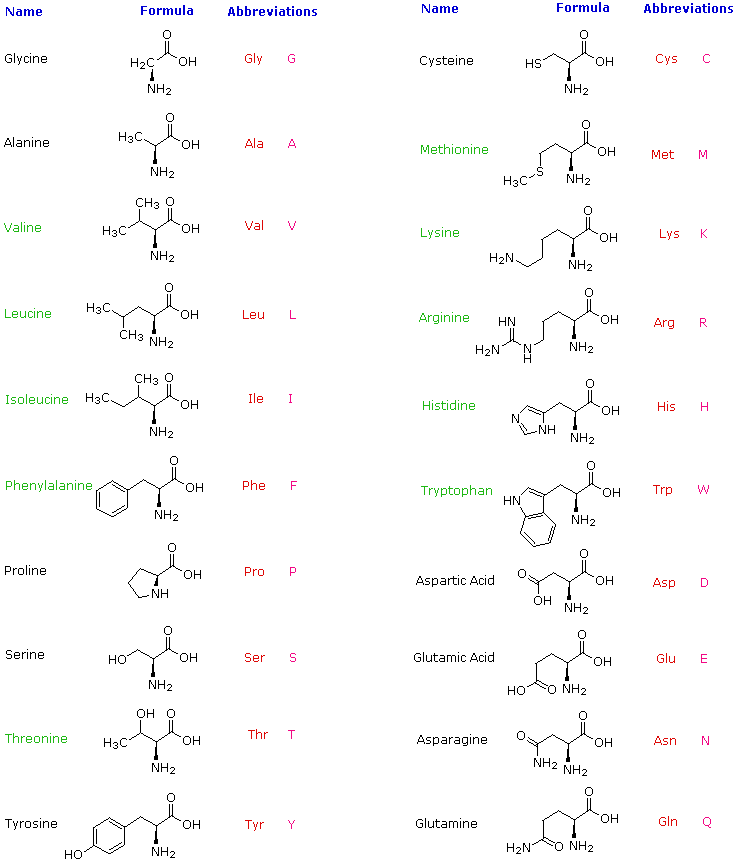

Some common features of these amino acids should be noted. With the exception of proline, they are all 1º-amines; and with the exception of glycine, they are all chiral. The configurations of the chiral amino acids are the same when written as a Fischer projection formula, as in the drawing on the right, and this was defined as the L-configuration by Fischer. The R-substituent in this structure is the remaining structural component that varies from one amino acid to another, and in proline R is a three-carbon chain that joins the nitrogen to the alpha-carbon in a five-membered ring. Applying the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog notation, all these natural chiral amino acids, with the exception of cysteine, have an S-configuration. For the first seven compounds in the left column the R-substituent is a hydrocarbon. The last three entries in the left column have hydroxyl functional groups, and the first two amino acids in the right column incorporate thiol and sulfide groups respectively. Lysine and arginine have basic amine functions in their side-chains; histidine and tryptophan have less basic nitrogen heterocyclic rings as substituents. Finally, carboxylic acid side-chains are substituents on aspartic and glutamic acid, and the last two compounds in the right column are their corresponding amides.
The formulas for the amino acids written above are simple covalent bond representations based upon previous understanding of mono-functional analogs. The formulas are in fact incorrect. This is evident from a comparison of the physical properties listed in the following table. All four compounds in the table are roughly the same size, and all have moderate to excellent water solubility. The first two are simple carboxylic acids, and the third is an amino alcohol. All three compounds are soluble in organic solvents (e.g. ether) and have relatively low melting points. The carboxylic acids have pKa's near 4.5, and the conjugate acid of the amine has a pKa of 10. The simple amino acid alanine is the last entry. By contrast, it is very high melting (with decomposition), insoluble in organic solvents, and a million times weaker as an acid than ordinary carboxylic acids.
|
Compound |
Formula |
Mol.Wt. |
Solubility in Water |
Solubility in Ether |
Melting Point |
pKa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| isobutyric acid | (CH3)2CHCO2H | 88 | 20g/100mL | complete | -47 ºC | 5.0 |
| lactic acid | CH3CH(OH)CO2H | 90 | complete | complete | 53 ºC | 3.9 |
| 3-amino-2-butanol | CH3CH(NH2)CH(OH)CH3 | 89 | complete | complete | 9 ºC | 10.0 |
| alanine | CH3CH(NH2)CO2H | 89 | 18g/100mL | insoluble | ca. 300 ºC | 9.8 |


|
|
|
|
صنع الذكريات والتفكير يدمر الدماغ.. دراسة تشرح السبب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الصين.. عودة كاسحتي الجليد إلى شنغهاي بعد انتهاء بعثة استكشافية إلى القطب الجنوبي
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تكرم الفائزين بأبحاث طلبة كلية الصيدلة وطب الأسنان
|
|
|
|
مشروع التكليف الشرعي بنسخته السادسة الورود الفاطمية... أضخم حفل لفتيات كربلاء
|
|
|
|
ضمن جناح جمعيّة العميد العلميّة والفكريّة المجمع العلمي يعرض إصداراته في معرض تونس الدولي للكتاب
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تعقد مؤتمرها الطلابي العلمي الرابع
|