
Doppler Effect
 المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
 المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
p43
الجزء والصفحة:
p43
 28-2-2016
28-2-2016
 1913
1913
Doppler Effect
Regardless of the frequency of electromagnetic waves, they are subject to the Doppler effect. The Doppler effect causes the observed frequency of radiation from a source to differ from the actual radiated frequency if there is motion that is increasing or decreasing the distance between the source and the observer. The same effect is readily observable as variation in the pitch of sound between a moving source and a stationary observer, or vice versa.
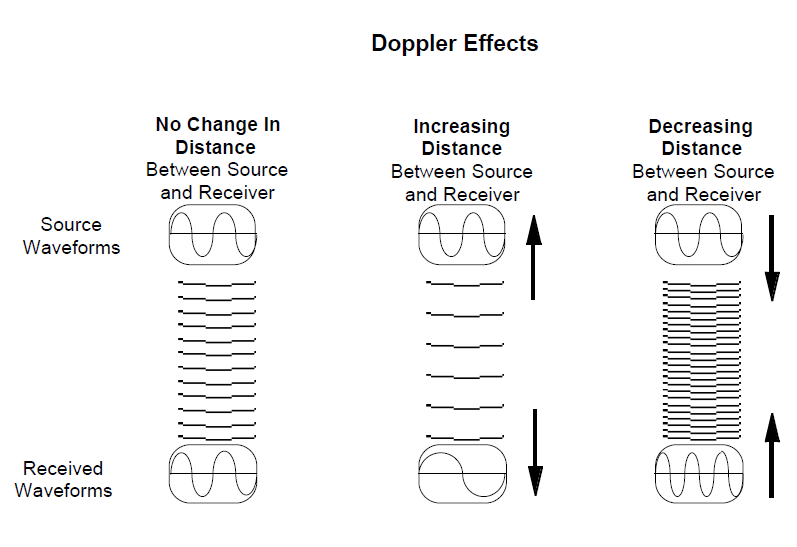
When the distance between the source and receiver of electromagnetic waves remains constant, the frequency of the source and received wave forms is the same. When the distance between the source and receiver of electromagnetic waves is increasing, the frequency of the received wave forms is lower than the frequency of the source wave form. When the distance is decreasing, the frequency of the received wave form will be higher than the source wave form.
The Doppler effect is very important to both optical and radio astronomy. The observed spectra of objects moving through space toward Earth are shifted toward the blue (shorter wavelengths, (while objects moving through space away from Earth are shifted toward the red. The Doppler effect works at all wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Thus, the phenomenon of apparent shortening of wavelengths in any part of the spectrum from a source that is moving toward the observer is called blue shifting, while the apparent lengthening of wavelengths in any part of the spectrum from a source that is moving away from the observer is called red shifting.
Relatively few extraterrestrial objects have been observed to be blue shifted, and these, it turns out, are very close by, cosmically speaking. Examples are planets in our own solar system with which we are closing ranks due to our relative positions in our orbits about the sun, some other objects in our galaxy, some molecular clouds, as well as some galaxies in what is termed the local group of galaxies.
Almost all other distant objects are red shifted. The red shifting of spectra from very distant objects is due to the simple fact that the universe is expanding. Space itself is expanding between us and distant objects, thus they are moving away from us. This effect is called cosmic red shifting, but it is still due to the Doppler effect.
Distances to extragalactic objects can be estimated based in part on the degree of red shifting of their spectra. As the universe expands, all objects recede from one another at a rate proportional to their distances. The Hubble Constant relates the expansion velocity to the distance and is most important for estimating distances based on the amount of red shifting of radiation from a source. Our current estimate for the Hubble Contant is 60-80 km/s per million parsecs (1 parsec = 3.26 light years).
The spectra from quasars, for example, are quite red-shifted. Along with other characteristics, such as their remarkable energy, this red shifting suggests that quasars are the oldest and most distant objects we have observed. The most distant quasars appear to be receding at over 90% the speed of light!
 الاكثر قراءة في الصوت
الاكثر قراءة في الصوت
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


