

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
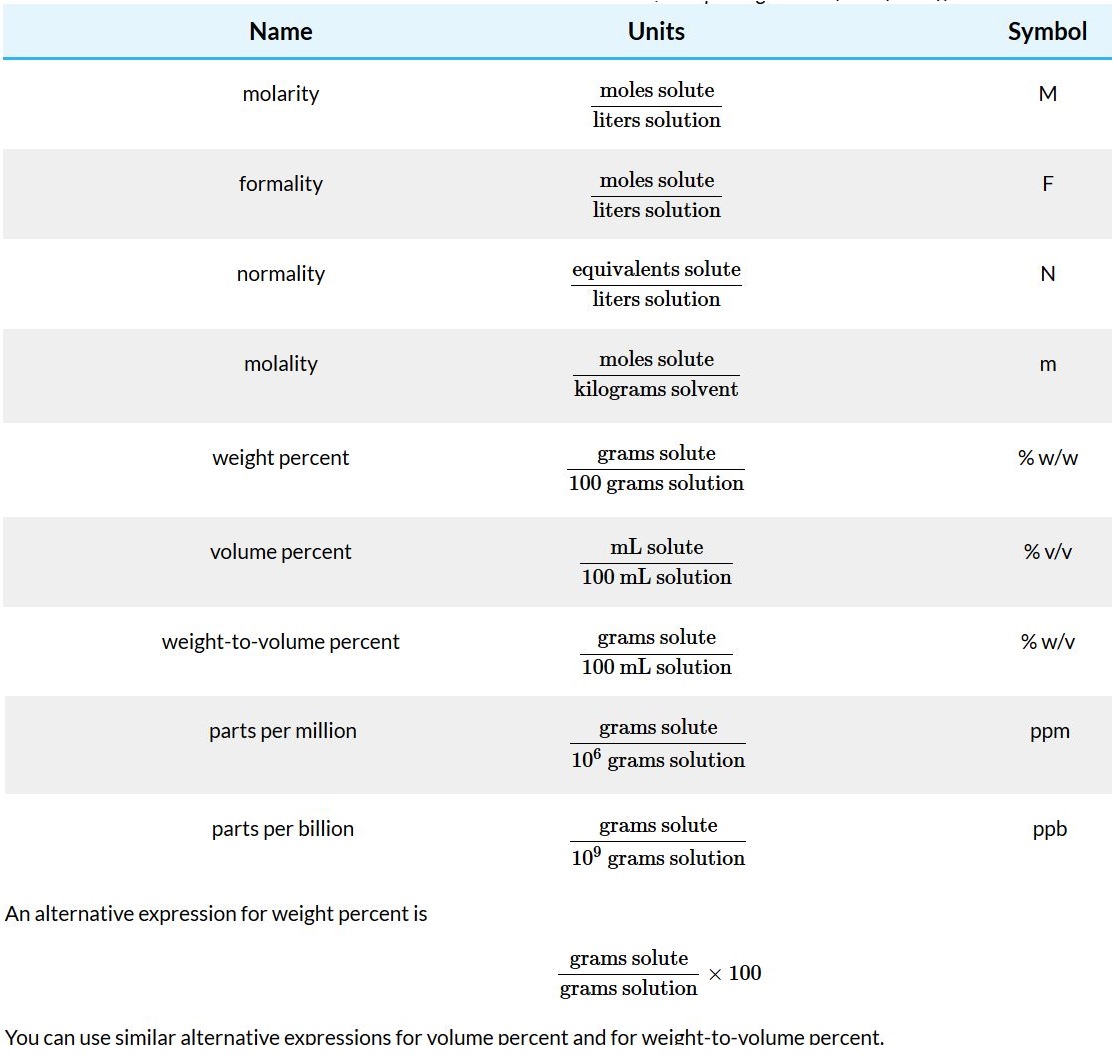
Molarity and Formality
المؤلف:
........
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
............
21-5-2019
5429
Molarity and Formality
Both molarity and formality express concentration as moles of solute per liter of solution. There is, however, a subtle difference between molarity and formality. Molarity is the concentration of a particular chemical species. Formality, on the other hand, is a substance’s total concentration without regard to its specific chemical form. There is no difference between a compound’s molarity and formality if it dissolves without dissociating into ions. The formal concentration of a solution of glucose, for example, is the same as its molarity. (A solution that is 0.0259 M in glucose is 0.0259 F in glucose as well.)
For a compound that ionizes in solution, such as NaCl , molarity and formality are different. Dissolving 0.1 moles of CaCl2 in 1 L of water gives a solution containing 0.1 moles of Ca2+ and 0.2 moles of Cl−. The molarity of NaCl, therefore, is zero since there is essentially no undissociated NaCl. The solution, instead, is 0.1 M in Ca2+ and 0.2 M in Cl−. The formality of NaCl, however, is 0.1 F since it represents the total amount of NaCl in solution. The rigorous definition of molarity, for better or worse, is largely ignored in the current literature, as it is in this textbook. When we state that a solution is 0.1 M NaCl we understand it to consist of Na+ and Cl− ions. The unit of formality is used only when it provides a clearer description of solution chemistry.
Molarity is used so frequently that we use a symbolic notation to simplify its expression in equations and in writing. Square brackets around a species indicate that we are referring to that species’ molarity. Thus, [Na+] is read as “the molarity of sodium ions.”
 الاكثر قراءة في التحليل النوعي والكمي
الاكثر قراءة في التحليل النوعي والكمي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















