


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 26-8-2019
Date: 24-9-2020
Date: 10-9-2020
|
Characteristics of the SN2 Reaction
Now that we know how SN2 reactions occur, we need to see how they can be used and what variables affect them. Some SN2 reactions are fast, and some are slow; some take place in high yield and others in low yield. Understanding the factors involved can be of tremendous value. Let’s begin by recalling a few things about reaction rates in general.
The rate of a chemical reaction is determined by the activation energy ΔG‡, the energy difference between reactant ground state and transition state. A change in reaction conditions can affect ΔG‡ either by changing the reactant energy level or by changing the transition-state energy level. Lowering the reactant energy or raising the transition-state energy increases ΔG‡ and decreases the reaction rate; raising the reactant energy or decreasing the transition state energy decreases ΔG‡ and increases the reaction rate (Figure 1.1). We’ll see examples of all these effects as we look at SN2 reaction variables.
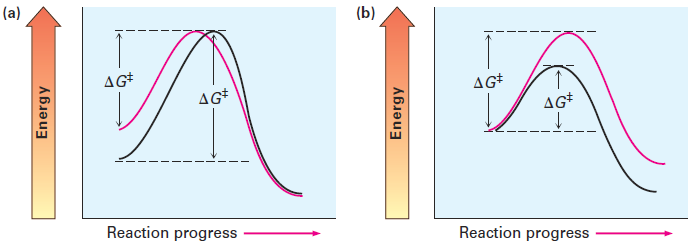
Figure 1.1 The effects of changes in reactant and transition-state energy levels on reaction rate. (a) A higher reactant energy level (red curve) corresponds to a faster reaction (smaller ΔG‡). (b) A higher transition-state energy level (red curve) corresponds to a slower reaction (larger ΔG‡).


|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي يقيم دورة تطويرية عن أساليب التدريس ويختتم أخرى تخص أحكام التلاوة
|
|
|