


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 8-12-2016
Date: 6-2-2021
Date: 26-10-2020
|
Phase and Amplitude
The Equation (i) for a traveling wave can be generalized by noting that the wave can have an arbitrary amplitude A,
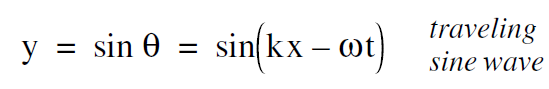 .......(i)
.......(i)
and an arbitrary constant phase angle ∅ to give
y = A sin (kx – ωt + ∅) .....(1)
The amplitude A just makes the sine wave bigger or smaller, and the phase angle ∅ shifts the sine wave to the left or right.
To see precisely how the phase angle ∅ shifts the sine wave, we have in Figure (1) compared sin θ and sin (θ + ∅) . The function sin (θ + ∅) crosses zero when the angle (θ + ∅) = 0 or at (θ = – ∅) . Thus adding a phase angle ∅ shifts the sine wave back a distance – ∅ radians. If, for example, we set ∅ = π/2 , the wave is shifted back 1/4 of a wavelength, and we have converted a sine wave into a cosine wave.
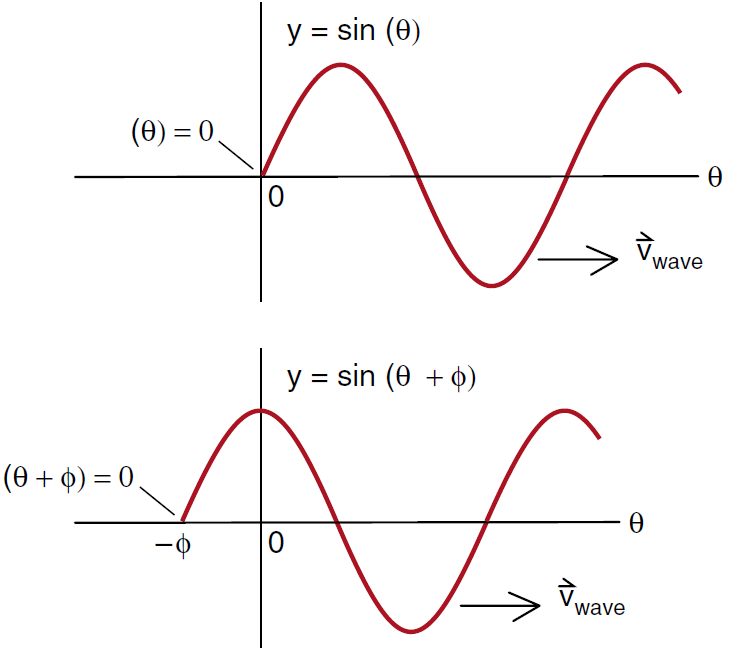
Figure 1: Adding a phase angleφ shifts the wave back a distanceφ .



|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقيم ندوة علمية عن روايات كتاب نهج البلاغة
|
|
|