

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies
Use of language
المؤلف:
Janet Tod and Sue Soan
المصدر:
Additional Educational Needs
الجزء والصفحة:
P178-C12
2025-04-26
291
Use of language
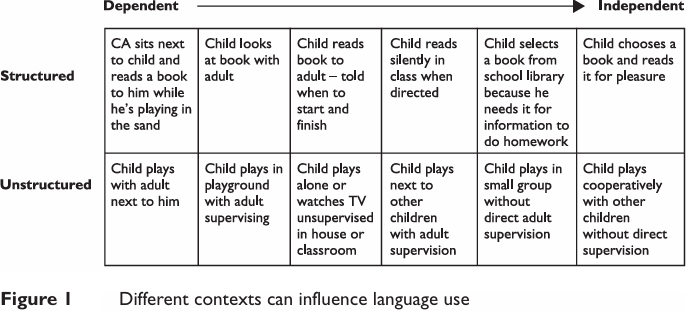
Obviously use of language is influenced by the social context. A child may well use language differently in a one-to-one structured setting in which the adult can give time and support to social communication. Figure 1 illustrates different contexts that may influence language use in the primary classroom.
This framework for social communication states that important variables include:
■ number of people involved in the communication;
■ amount of adult intervention;
■ type of activity: structured vs unstructured;
■ amount of social interaction required;
■ degree of autonomy needed.
It is important that staff work together when assessing the educational and social needs of pupils with SLCN. Keeping brief notes about the pupil’s response to support is crucial to effective monitoring and evaluation. Schools, quite appropriately, embed the assessment of SLCN within the whole-school framework for assessment. Assessment of progress in some curricular areas is particularly relevant in identifying the needs of pupils with SLCN. These include National Curriculum English ‘Speaking and Listening’ and the different levels that make up the framework of the National Literacy Strategy:
■ word level: phonics, spelling and vocabulary;
■ sentence level: grammar and punctuation;
■ text level: comprehension and composition.
Discussion
■ What do you consider the main purposes of assessment for learners with SLCN in your own setting?
■ How do you contribute to the assessment process in your own setting?
■ What effect does your assessment of pupil response to your support have on your own behavior?
■ How might you bring about improvements in using collaborative approaches to assessment to improve provision for learners with SCLN in your own setting?
■ To what extent do you involve the pupil in assessment of his/her learning?















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















