
آخر المواضيع المضافة


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 23-8-2021
Date: 2-1-2022
Date: 13-12-2021
|
Oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate in TCA
Isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyzes the irreversible oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate, yielding the first of three NADH molecules produced by the cycle and the first release of CO2 (Fig. 1). This is one of the rate-limiting steps of the TCA cycle.
The enzyme is allosterically activated by ADP (a low-energy signal) and Ca2+ and is inhibited by ATP and NADH, levels of which are elevated when the cell has abundant energy stores.
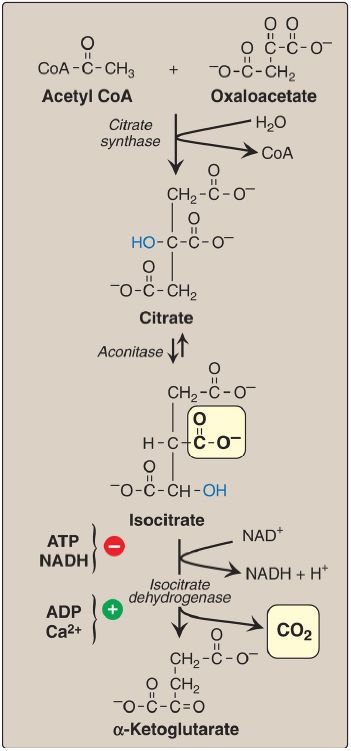
Figure 1: Formation of α-ketoglutarate from acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) and oxaloacetate. NAD(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; CO2 = carbon dioxide.

|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تنظّم دورةً حول آليّات الذكاء الاصطناعي لملاكاتها
|
|
|